Differences Between HILIC Columns and ANP Columns
Introduction: When separating highly polar analytes, two approaches are most commonly considered: Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography (HILIC) and Aqueous Normal Phase (ANP).
While both often begin with high‑organic mobile phases and use “inverse” gradients, they do not rely on the same retention mechanism and they behave very differently in day‑to‑day work. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right column and method—especially for LC‑MS workflows.
1) Retention Mechanism
- HILIC: Retention is dominated by partitioning into a semi‑permanent, water‑rich layer that forms on the surface of ordinary silica or polar phases. This hydration shell can vary with temperature, buffer strength, and recent gradient history, which is a frequent source of drift.
- ANP (on Cogent TYPE‑C™ silica hydride): The silica‑hydride surface does not support a persistent water layer, leading to a different retention process that behaves more like local solvent displacement rather than classic HILIC partitioning. This underpins faster mass transfer, less drift, and more reproducible retention.
For a foundational perspective distinguishing HILIC vs. ANP mechanisms, see the comparative discussion by Pesek & Matyska.
2) Equilibration and Throughput
- HILIC: Because the water layer must rebuild and stabilize after gradients, equilibration is slow. Labs often experience significant downtime between runs, which limits throughput—particularly in gradient methods.
- ANP: On TYPE‑C™ columns, re‑equilibration is rapid (commonly 3–5 column volumes), supporting fast sequences and even ballistic gradients (sub‑minute to ~5‑minute methods) with excellent run‑to‑run precision.
3) Salt Requirements & LC‑MS Compatibility
- HILIC: Many methods require high, sometimes 50–100 mM, salt to tune retention—effective for selectivity but problematic for LC‑MS (ion suppression, fouling) and for preparative recovery.
- ANP: Typically operates with ≤15 mM salts (often 5–15 mM) and can avoid non‑volatile buffers, which improves MS signal stability, reduces instrument maintenance, and speeds cleanup in prep workflows.
4) Precision, Robustness, and Column Lifetime
- HILIC: The variable hydration shell can cause retention‑time variability and reproducibility issues; some users report unexpected column failures during long sequences.
- ANP: TYPE‑C™ silica hydride phases exhibit extraordinary retention‑time precision and robustness, with markedly longer lifetimes reported vs. typical HILIC phases under comparable use.
5) Selectivity & Analyte Scope
- HILIC: Excellent for many polar/ionic analytes but can struggle with certain strong acids/bases because of interactions with ionized silanols on silica, especially as pH rises.
- ANP: Retains polar compounds and can retain some non‑polar species on the same column (dual‑mode capability), expanding selectivity space and simplifying method development. Strong sulfonic acids and other difficult polar analytes are often retained better and more reproducibly than in HILIC.
6) Ballistic Gradients & High‑Speed Methods
If your workflow demands very fast LC‑MS cycles, ANP on TYPE‑C™ columns is typically the safer, more precise choice, because the stationary phase does not rely on a slowly regenerating water layer. This allows aggressive gradients and short columns while maintaining precision.
Practical Takeaways
- For high‑throughput LC‑MS with polar analytes: Start with ANP on Cogent TYPE‑C™ columns; expect fast equilibration, low salt, and stable precision.
- If you must run HILIC: plan for longer equilibration, careful control of temperature and salts, and more frequent verification of retention‑time stability.
🟢Summary
ANP vs. HILIC — what’s the real difference? HILIC relies on a hydration shell on conventional silica that drives partitioning‑based retention; this layer changes with conditions and slows equilibration, which can reduce throughput and precision—often with high salt levels that complicate LC‑MS. ANP on Cogent TYPE‑C™ silica hydride uses a different surface (no persistent water layer), enabling fast re‑equilibration (3–5 CV), low‑salt, LC‑MS‑friendly operation, excellent retention‑time precision, and longer column life.
ANP can also retain polar and some non‑polar analytes on the same column, streamlining method development and delivering reliable performance for modern regulated labs.
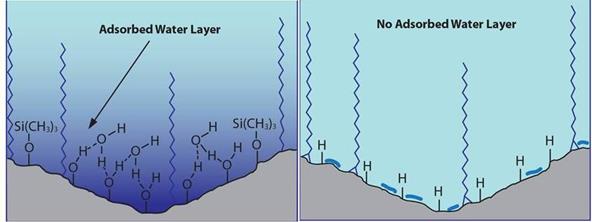
HILIC Phases have a Water Shell Cogent TYPE-C Silica has no Water Shell
See also: Comparison of the efficiency in ANP vs. HILIC.
See also: Wikipedia definition of ANP
See also: ANP v. HILIC Advantages
A very popular journal article on this subject:
Journal of Chromatography A, E. Barto, A. Felinger & P. Jandera Investigation of the temperature dependence of water adsorption on silica-based stationary phases in hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography, 2017, Volume 1489 pages 143-149

