There are significant differences between HILIC columns and Cogent TYPE-C™ Silica Hydride columns, though both can separate polar compounds. Here are the key points:
Similarities:
Both HILIC and Cogent TYPE-C™ columns retain polar compounds when using mobile phases with high organic content (>70%). Each operates on principles related to normal-phase chromatography—HILIC is classified as “Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography,” while Cogent columns use Aqueous Normal Phase (ANP). Both can retain analytes that reversed-phase columns cannot.
Differences:
- Stationary Phase Polarity: HILIC phases are highly polar, whereas TYPE-C™ phases are relatively non-polar.
- Retention Profile: HILIC columns do not retain non-polar compounds, while Cogent columns can retain both polar and many non-polar compounds—sometimes in the same gradient or isocratic run.
-
Mechanism:
- HILIC relies on a hydration layer on the silica surface. Polar analytes partition into this layer and interact with silanols beneath it. This requires careful equilibration for reproducibility.
- Cogent TYPE-C™ columns lack significant silanols and hydration shells. Retention of polar compounds occurs via adsorption on the silica hydride surface, while bonded phases allow non-polar retention. This design enables rapid equilibration and fast gradient changes.
- Versatility: HILIC columns are limited to HILIC mode. Cogent TYPE-C™ columns can switch seamlessly between ANP, RP, and traditional Normal Phase (using non-polar solvents like hexane) without hysteresis.
This flexibility makes Cogent TYPE-C™ columns uniquely efficient for complex separations. Additional features and benefits are detailed in other Knowledge Base article s.
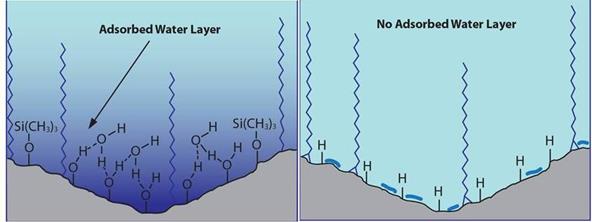
HILIC Phases have a Water Shell Cogent TYPE-C Silica has no Water Shell
See also: Comparison of the efficiency in ANP vs. HILIC.See also: Wikipedia definition of ANP
See also: ANP v. HILIC Advantages
A very popular journal article on this subject:
Journal of Chromatography A, E. Barto, A. Felinger & P. Jandera Investigation of the temperature dependence of water adsorption on silica-based stationary phases in hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography, 2017, Volume 1489 pages 143-149

